Genetic Inheritance
This page is also available as a printable PDF: Genetic Inheritance
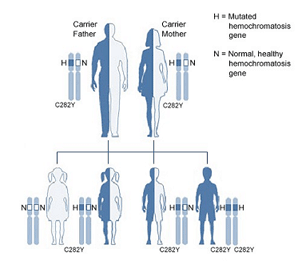
Inheritance Combinations for HFE Hemochromatosis (Autosomal Recessive Inheritance)
If both parents are carriers of one C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, for each pregnancy there is a 25% chance of inheriting two normal copies of the gene and being unaffected, a 50% chance of inheriting one mutated copy and one normal copy and being a carrier, and a 25% chance of inheriting two mutated copies and being affected.
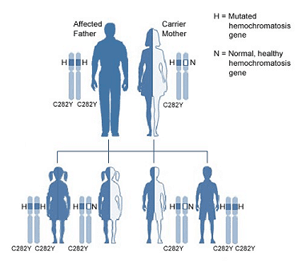
If one parent is affected with two copies of the C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is unaffected, there is a 100% chance that each pregnancy will inherit one mutated copy and one normal copy, which means that all offspring will be obligate carriers.

If one parent is affected with two copies of the C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is a carrier for one C282Y mutation, for each pregnancy there is a 50% chance of inheriting one mutated copy and one normal copy and being a carrier, and a 50% chance of inheriting two mutated copies and being affected.
If one parent is affected with two copies of the C282Y mutation for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is a carrier for one H63D mutation, for each pregnancy there is a 50% chance of inheriting one mutated C282Y copy and one normal copy and being a carrier, and a 50% chance of inheriting two mutated copies (one C282Y and one H63D) and being affected.

If one parent is affected with two mutated copies (one C282Y and one H63D) for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is unaffected, there is a 100% chance that each pregnancy will inherit one mutated copy and one normal copy, which means that all offspring will be obligate carriers. 50% of the offspring will be C282Y carriers and 50% of the offspring will be H63D carriers.

If one parent is affected with two mutated copies (one C282Y and one H63D) for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is a carrier for one C282Y mutation, for each pregnancy: there is a 50% chance of inheriting one mutated copy (either one C282Y or one H63D) and one normal copy and being a carrier, and a 50% chance of inheriting two mutated copies (either two C282Y copies, or one C282Y and one H63D) and being affected.

If one parent is affected with two mutated copies (one C282Y and one H63D) for the HFE-hemochromatosis gene, and the other parent is a carrier for one H63D mutation, for each pregnancy: there is a 50% chance of inheriting one mutated copy (either one C282Y or one H63D) and one normal copy and being a carrier, and a 50% chance of inheriting two mutated copies (either two H63D copies, or one C282Y and one H63D) and being affected.

Types of Hemochromatosis
There are 4 types of hemochromatosis with differing characteristics: Type 1, Type 2 (A and B), Type 3 and Type 4.
| Type 1 | Type 2A | Type 2B | Type 3 | Type 4 | |
| Name | Classic HHC | Juvenile HHC | Juvenile HHC | TfR2-related HHC | Ferroportin-related iron overload |
| Gene | HFE | HJV | HAMP | TfR2 | SLC40A1 |
| Protein Produced | HFE | Hemojuvelin | Hepcidin | Transferrin receptor 2 | Ferroportin (iron regulatory protein) |
| Inheritance | autosomal recessive | autosomal recessive | autosomal recessive | autosomal recessive | autosomal dominant |
| Function | interruption of transferrin-bound iron, possible modulation of hepcidin regulation | unknown; possible hepcidin modulation | regulation of iron release in intestinal and blood cells | possible interference of iron uptake by liver cells | possible interference of iron export from intestinal, liver and placental cells |
| Organ Damage | variable | high | high | variable | low |
| Age of Onset | 40s or 50s | 20s or 30s | 20s or 30s | 40s or 50s | 40s or 50s |
Adapted from New England Journal of Medicine, 350; 23, June 3, 2004: Classifications as defined by OMIM (Online Mendelaian Inheritance in Man)
There may be other as yet unknown functions related to iron overload. The listed functions do not, at least at this time, always account for the known pathophysiological features associated with gene mutation.